Rise of Fraudulent Loan Apps During Covid
In the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic from 2020 and its subsequent decline, there has been a notable surge in fraud cases, particularly revolving around counterfeit fintech apps offering loans. Individuals unsuspectingly downloading these deceptive loan apps are not only falling victim to steep interest rates but also compromising personal data such as photos and contacts. There have been following media reports where some have even committed suicide:
- https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/instan-loan-apps-trap-torture-harassment-60-deaths-india-china-link-101697013563581.html
- https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/tamil-nadu-man-suicide-loan-app-executive-shared-nude-pictures-online-crime-2411960-2023-07-26
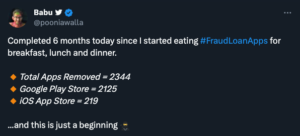
This has escalated into a relentless cat-and-mouse game, with the odds heavily favouring fraudsters. I have closely followed some great work done by folks like Babu Lal in getting these fake loan apps removed from the playstores:
Regulatory bodies are deflecting responsibility onto Play Stores, but I think that addressing this issue requires a collaborative effort between the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Non-Banking Financial Corporations (NBFCs), and Play Stores operated by industry giants like Google and Apple.
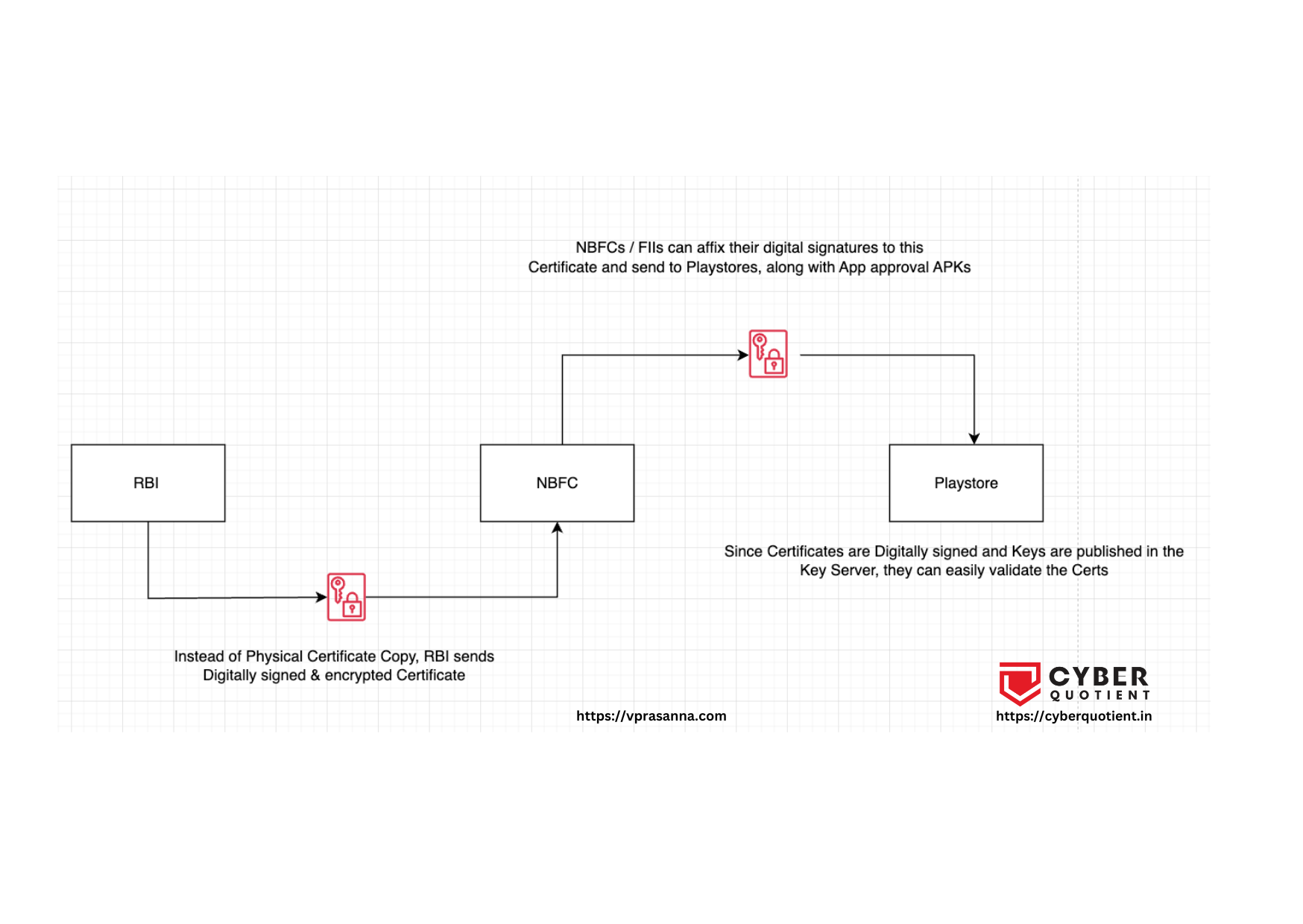
Play Stores employ a gating check for allowing fintech apps, which involves verifying the NBFC certificate issued by the RBI. This certificate is essentially a copy of the physical document provided by the RBI to NBFCs/Banks/Financial Instituitions.
What has come to my attention, through both extensive reading of various reports and first-hand encounters with similar incidents, is that:
Fraudsters are Fabricating copies of the RBI-issued NBFC certificates.
These fabricated copies are then submitted to Play Stores along with the mobile app applications. It’s essential to note that sharing this NBFC certificate is mandatory for apps to be categorised as financial apps.
In the case we encountered, it took a significant amount of time to get the fake app removed from the playstore. This was an OEM playstore and not the regular Google or Apple owned. The resolution ultimately necessitated pursuing the trademark infringement route.
The Solution:
One of the ways I thought this could be curbed or to an extent limited is by making use of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) setup with Digitally Signed Certificates + Encryption and using the good old PGP/GPG tools. PGP stands for Pretty Good Privacy and originally developed by Phil Zimmermann in 1991 as a proprietary software. While GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) was developed as an open-source alternative to PGP. GPG is essentially PGP with an open-source licence.Yeah, it’s free and has no impact monetarily on the smaller banks and financial institutions for easy adoption. Only a small learning curve in the beginning on usage of GPG, but it’s better than losing money.
The goal is to establish a robust system that ensures the integrity of certificates and prevents the submission of falsified documents to Play Stores, thereby mitigating financial losses and data leaks.
In the context of multiple stakeholders, this proposed solution aligns with the shared responsibility among Apple, Google, RBI, and NBFCs in addressing the rise of fraudulent fintech apps. Here’s a breakdown of the proposal:
1. Establish Dedicated Email Addresses and Publish Public Keys:
– All involved parties would create dedicated email addresses and publish their public keys into a Key Server. This ensures a secure and standardised communication channel.
2. RBI Digitally Signs Certificates for NBFCs:
– The RBI would be responsible for digitally signing certificates in the names of respective NBFCs, establishing a secure and verifiable authentication process.
3. Optional Encryption of Certificates for NBFCs:
– As an additional layer of security, the RBI could choose to encrypt these certificates with the respective NBFCs’ public keys while transmitting them, preventing potential Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks. The reason to make this optional is, there are situations these certificates are attached when interacting with regulators.
4. NBFCs/Fintechs Decrypt and Use Certificates:
– NBFCs and Fintechs would then decrypt these certificates using their private keys and utilise them for their intended purposes.
5. NBFCs/Fintechs Sign and Encrypt Certificates for Playstores:
– NBFCs and Fintechs, having used the certificates, would digitally sign them and encrypt them with Google’s public keys as part of the Mobile App application form.
6. Playstore Teams Validate and Approve Apps:
– Playstore teams can efficiently validate these digitally signed and encrypted certificates, facilitating a streamlined approval process. Automation could be implemented given the inherent security of digital signatures.
7. Preventing Submission of Fake Documents:
– The proposed system effectively prevents the submission of fraudulent documents, such as copies of physical certificates, by ensuring the authenticity and integrity of digital certificates.
I couldn’t think of any loopholes except for the fact that commercial viability of PGP seems to have taken a severe beating. But there is good old GPG software to the rescue. While there has been similar implementation using Blockchain, the biggest hurdle I anticipate is the adoption with the NBFCs and other Financial Institutions that may not be tech-savvy.
The onus of keeping the RBI provided Certificates will be on the NBFCs and they can be revoked by RBI if in case they are leaked.
This is just a high level idea and can be further customised to handle the technical challenges and as reiterated earlier, this is a:
Shared Responsibility between the Regulator: RBI & Others, Playstore: Google, Apple & other Playstores, and NBFC/Fintechs/FIIs/Banks.
Opening this to scrutiny by peers. Please let me know what you think..
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Google Apple
#fraudapps #fraudloanapps #loanappscams #loansharks #onlineloan #instantloan #loanpps #fintechfrauds